How To Install Cacti on Ubuntu 18.04
Cacti is a free and open-source web-based network monitoring tool designed as the front end application for the Round-Robin database tool (RRDtool). It allows users to poll the services at an interval of time and resulting in the graph format.
Cacti, in general, it is used to get a graph of CPU and network bandwidth utilization and monitors the network traffic by polling a router or switch over the SNMP protocol.
Here, we will see how to install Cacti on Ubuntu 18.04.
Prerequisites
Update the repository index using the apt command.
sudo apt update
Install Apache & MariaDB
Cacti run on top of the AMP server. So, install Apache, MySQL, and PHP packages on your machine.
sudo apt install -y apache2 mariadb-server mariadb-client php-mysql libapache2-mod-php
Install PHP Extensions
Additionally, you would need to install a few PHP extensions for the proper functioning of Cacti.
sudo apt install -y php-xml php-ldap php-mbstring php-gd php-gmp
Install SNMP
Also, install the SNMP and RRDtool on the server in case you want to monitor the Cacti server as well.
sudo apt install -y snmp php-snmp rrdtool librrds-perl
Database Tuning
Cacti recommend changing MySQL a few settings for better performances. So, edit the configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Add/Update the below settings in [mysqld] section.
collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_ci max_heap_table_size = 128M tmp_table_size = 64M join_buffer_size = 64M innodb_file_format = Barracuda innodb_large_prefix = 1 innodb_buffer_pool_size = 512M innodb_flush_log_at_timeout = 3 innodb_read_io_threads = 32 innodb_write_io_threads = 16 innodb_io_capacity = 5000 innodb_io_capacity_max = 10000
Set Timezone
As a mandatory requirement, we need to set the timezone in the PHP configuration file. So, edit the php.ini file depending on your PHP version.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.2/apache2/php.ini
AND
sudo nano /etc/php/7.2/cli/php.ini
Update your timezone as shown below.
date.timezone = US/Central memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 60
Restart MariaDB service.
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
Create Database
Create a database for Cacti installation.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Now, create a database for the Cacti installation.
create database cacti;
Grant permission to the newly created database.
GRANT ALL ON cacti.* TO cactiuser@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'cactipassword'; flush privileges; exit
The newly created database user (cactiuser) should have access to the mysql.time_zone_name Table. To do that, import the mysql_test_data_timezone.sql to mysql database.
sudo mysql -u root -p mysql < /usr/share/mysql/mysql_test_data_timezone.sql
Then, log in to MySQL.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Grant the permission to cactiuser.
GRANT SELECT ON mysql.time_zone_name TO cactiuser@localhost; flush privileges; exit
Install Cacti
Download the latest version of the Cacti package using wget command.
wget https://www.cacti.net/downloads/cacti-latest.tar.gz
Extract the Cacti archive using the tar command and move the extracted files to /opt directory.
tar -zxvf cacti-latest.tar.gz sudo mv cacti-1* /opt/cacti
Import the default Cacti database data to the Cacti database.
sudo mysql -u root -p cacti < /opt/cacti/cacti.sql
Edit the Cacti config file to specify the database type, database name, MySQL hostname, user, and password information.
sudo nano /opt/cacti/include/config.php
Make the changes accordingly.
/* make sure these values reflect your actual database/host/user/password */ $database_type = "mysql"; $database_default = "cacti"; $database_hostname = "localhost"; $database_username = "cactiuser"; $database_password = "cactipassword"; $database_port = "3306"; $database_ssl = false;
Edit the crontab file.
sudo nano /etc/cron.d/cacti
Add the following entry in the crontab so that Cacti can poll every five min.
*/5 * * * * www-data php /opt/cacti/poller.php > /dev/null 2>&1
Edit the Apache configuration file to perform the remote installation.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/cacti.conf
Use the following configuration.
Alias /cacti /opt/cacti
<Directory /opt/cacti>
Options +FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
<IfVersion >= 2.3>
Require all granted
</IfVersion>
<IfVersion < 2.3>
Order Allow,Deny
Allow from all
</IfVersion>
AddType application/x-httpd-php .php
<IfModule mod_php.c>
php_flag magic_quotes_gpc Off
php_flag short_open_tag On
php_flag register_globals Off
php_flag register_argc_argv On
php_flag track_vars On
# this setting is necessary for some locales
php_value mbstring.func_overload 0
php_value include_path .
</IfModule>
DirectoryIndex index.php
</Directory>
Enable the created virtual host.
sudo a2ensite cacti
Restart Apache services.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Create a log file and allow the Apache user (www-data) to write a data on to Cacti directory.
sudo touch /opt/cacti/log/cacti.log sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /opt/cacti/
Setup Cacti
Visit the following URL to begin the installation of Cacti.
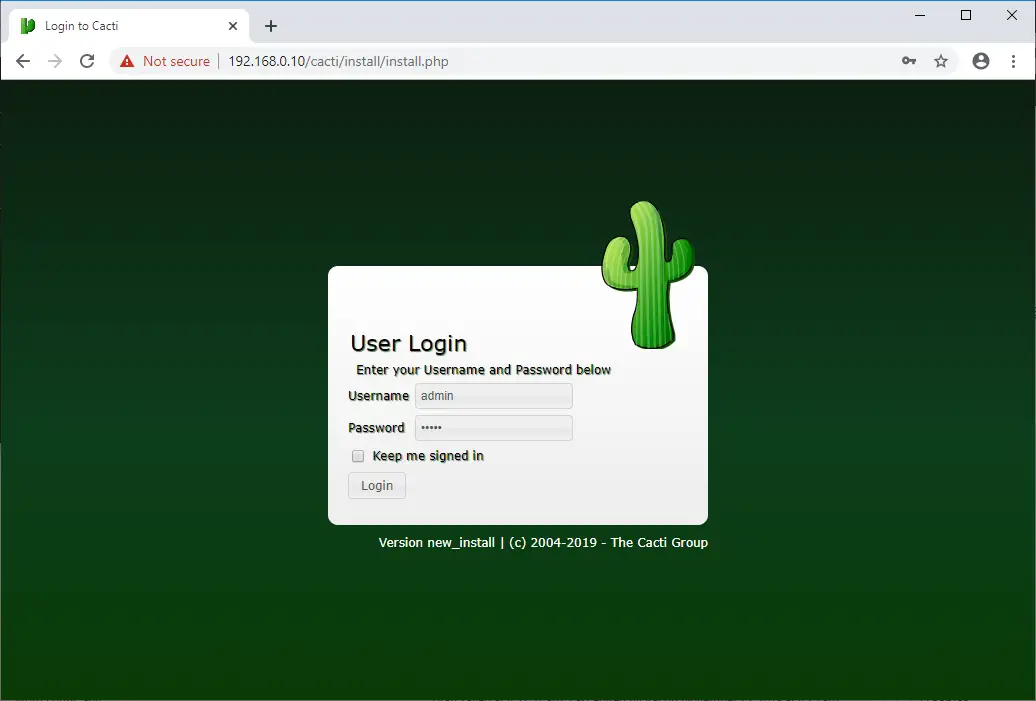
Login to Cacti to set up Cacti installation.
Username: admin
Password: admin
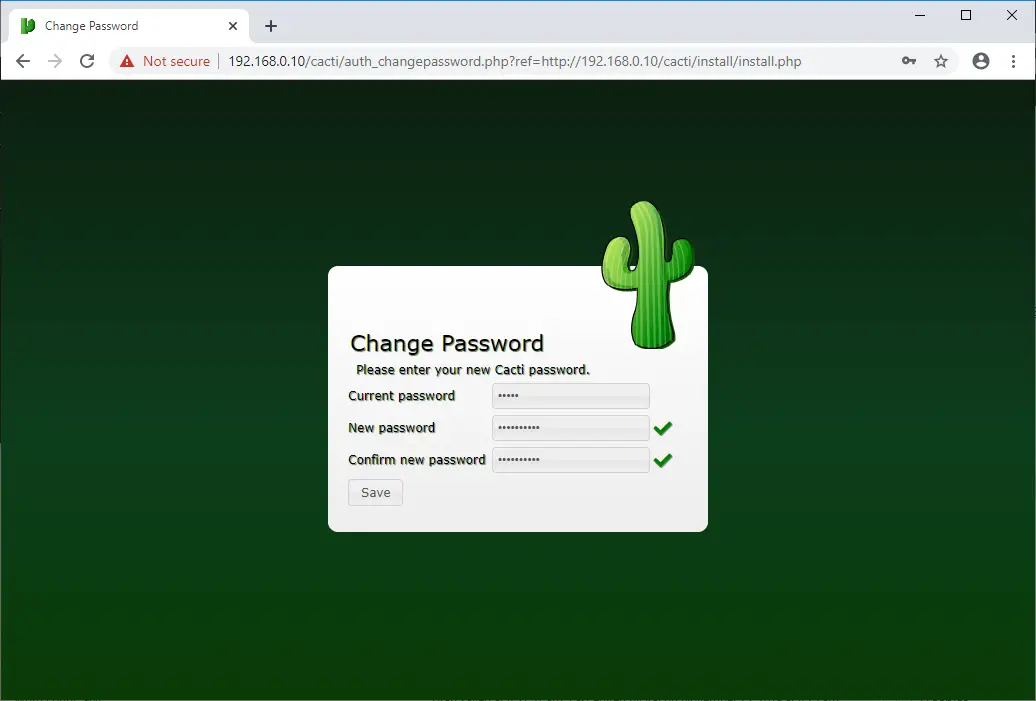
You must change the password of the Cacti admin user before you setup Cacti.
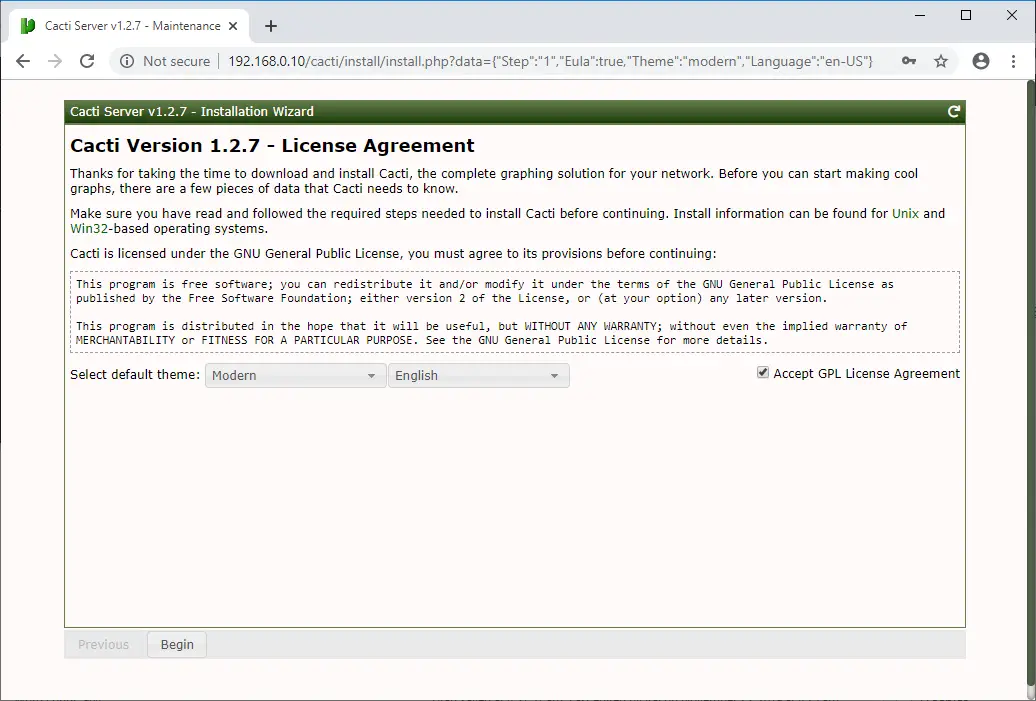
Accept the Cacti license agreement and click on Next to continue.
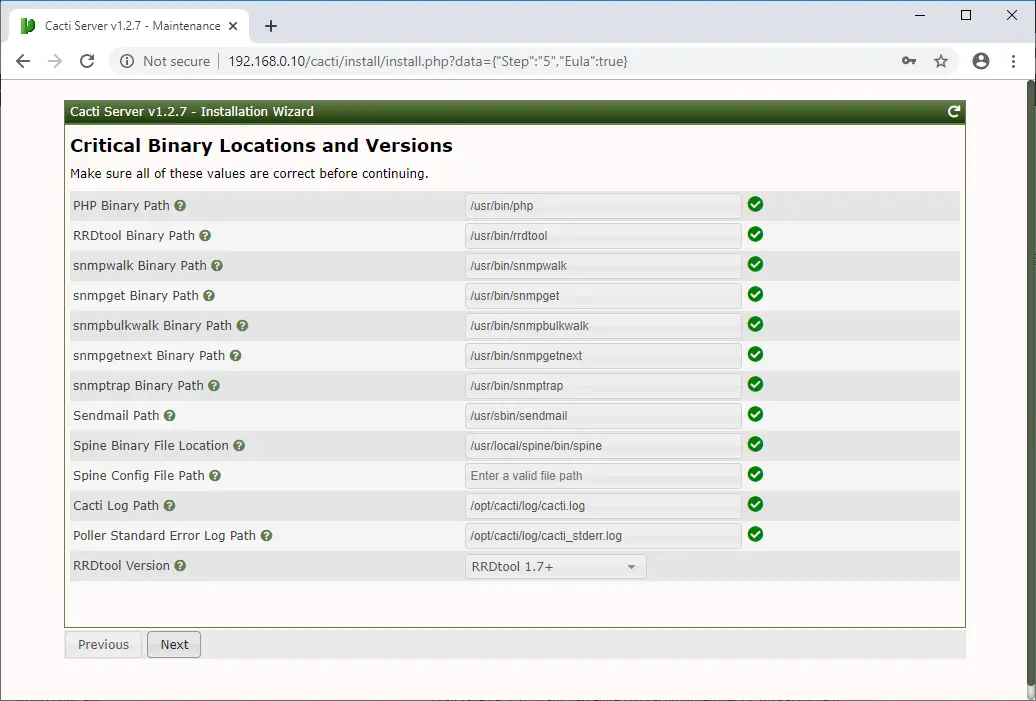
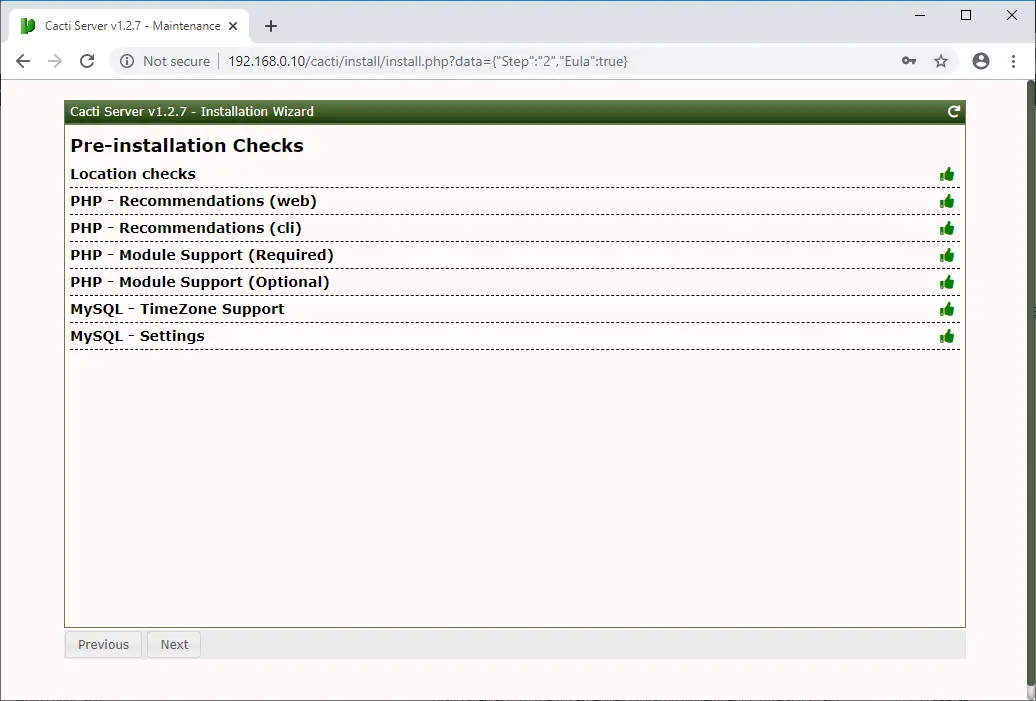
Cacti perform pre-installation checks and reports any issues on this page. You need to fix the problems if the installation wizard reports.
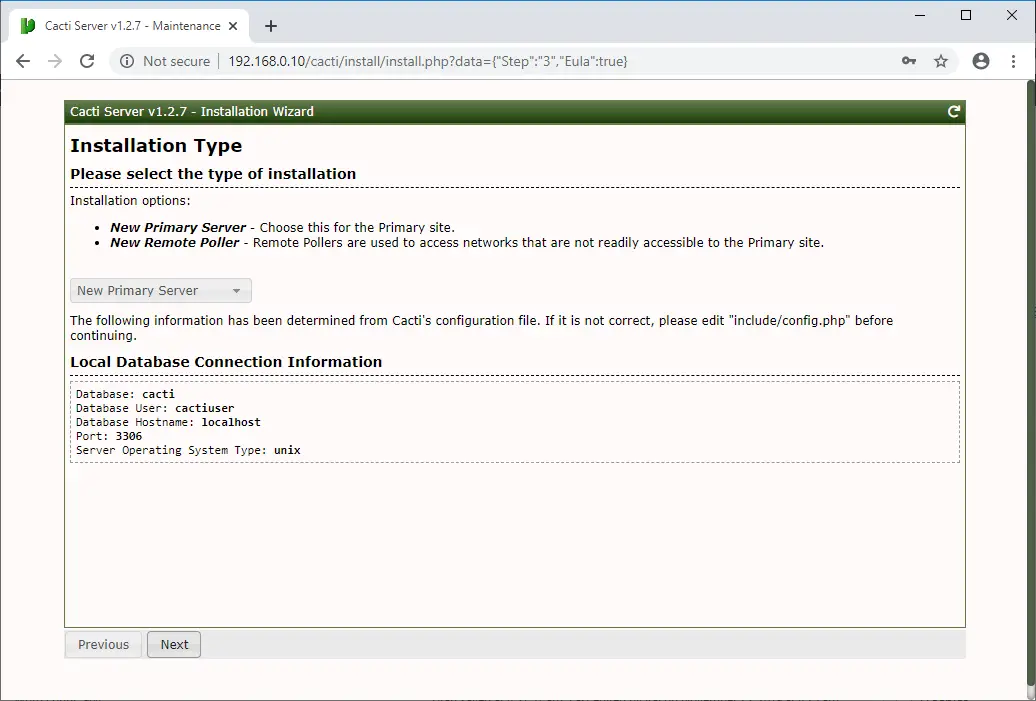
Select New Primary Server as an installation type for the new installation and then click Next.
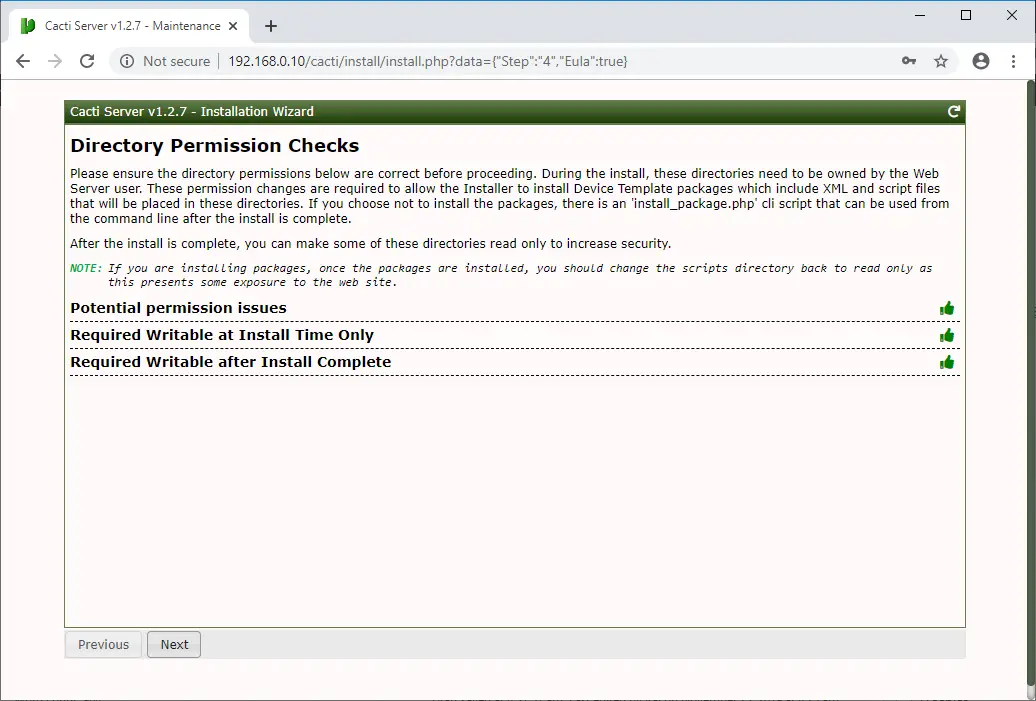
Now, Cacti installation wizard checks and reports for permission problems you may have in the Cacti installation directories.
It will show you here if there is any package is missing, which is mandatory for the Cacti.
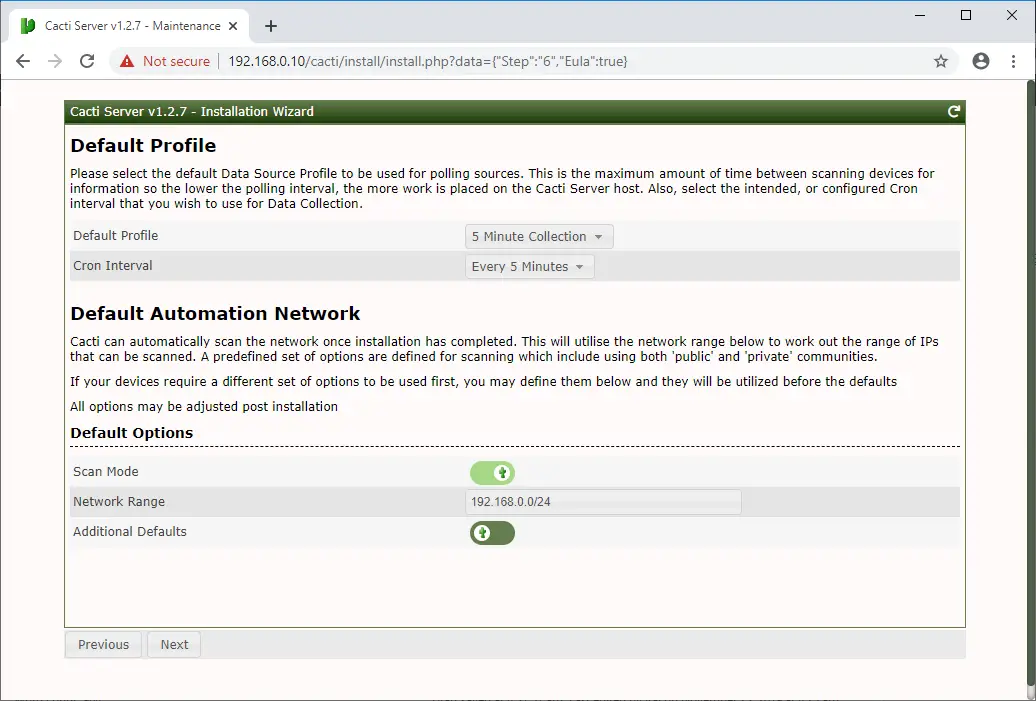
Click Next on the default profile page as we already configured cron to poll every five minutes.
Select all templates or the one you want and then click Finish to complete the installation of Cacti.
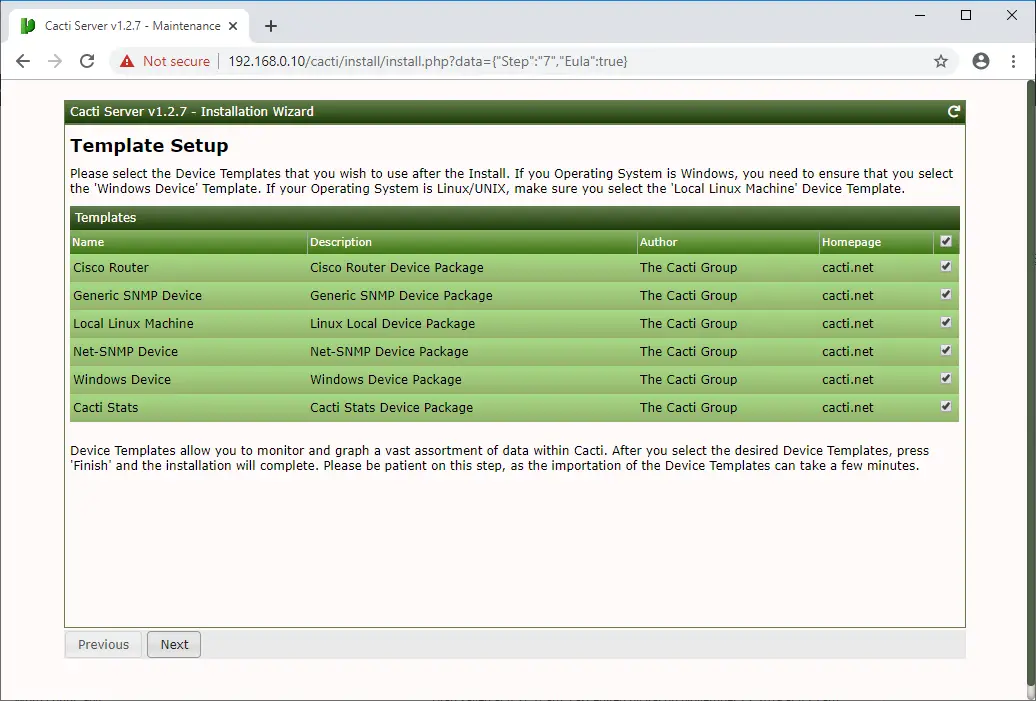
Click Next on the final test summary page.
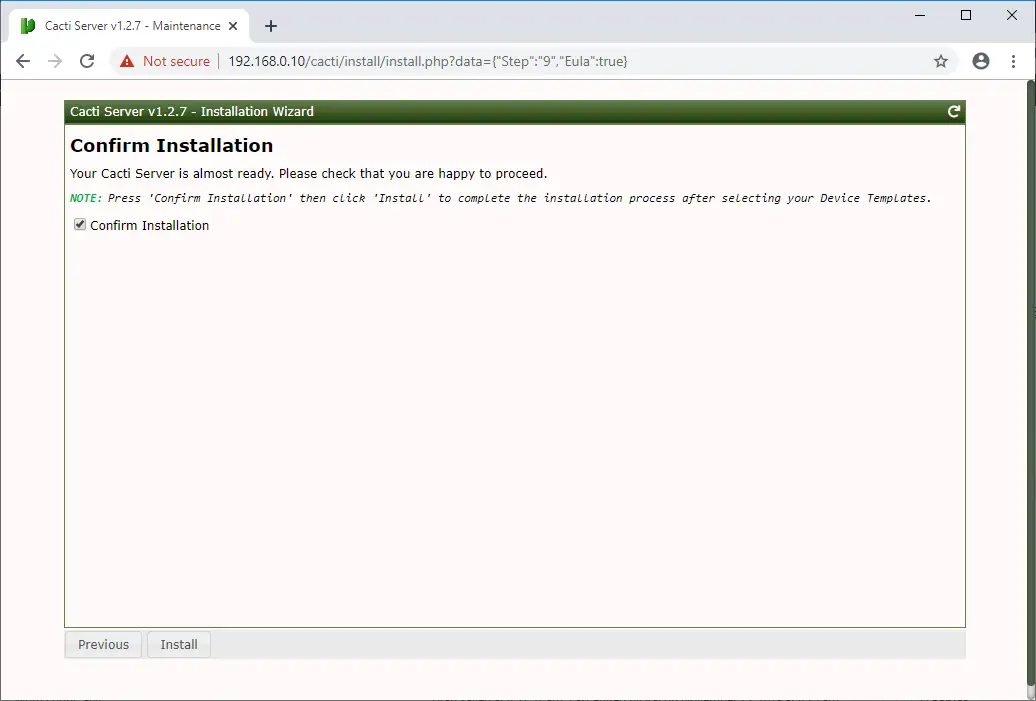
Select Confirm Installation and press Install to begin the Cacti installation.
Wait for the installation to complete.
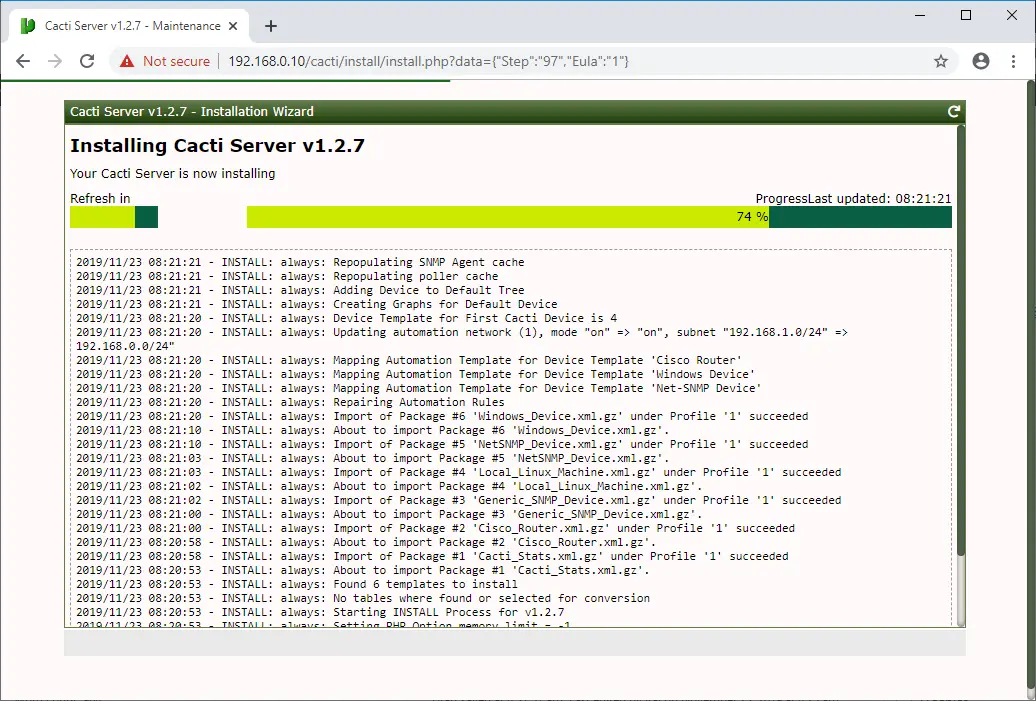
In a minute or two, the Cacti installation will complete.
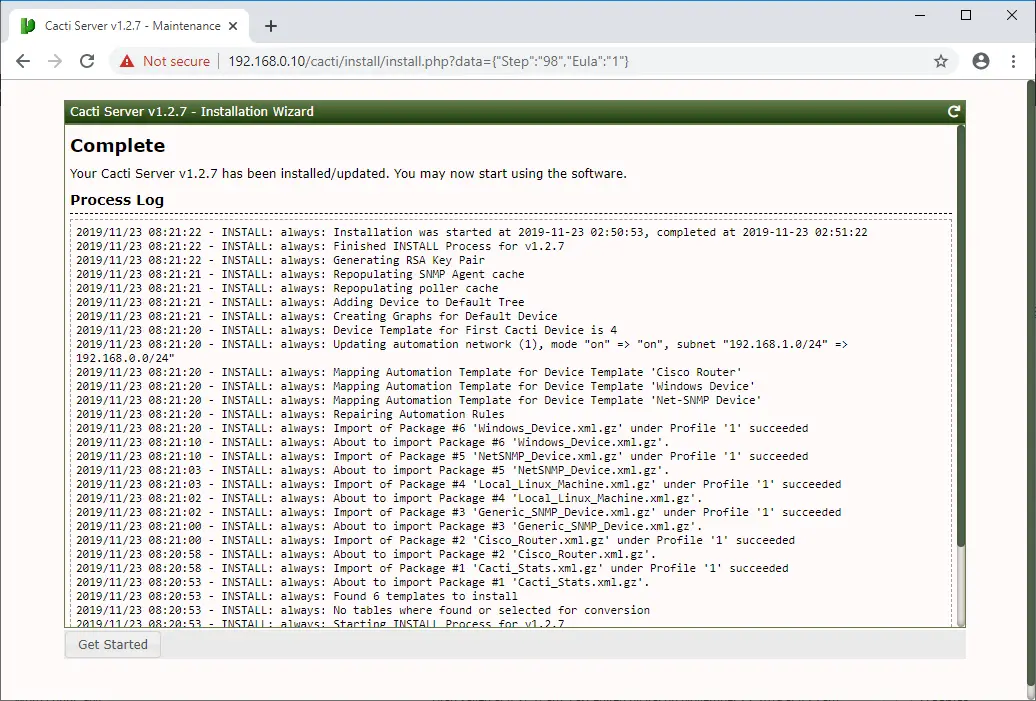
Clicking on the Get Started on the above page will take you directly to the Cacti dashboard. Otherwise, you can log in to Cacti with the user name and the password you set during the Cacti installation.
Access Cacti Dashboard
Enter User Name and Password to login to Cacti.
Password: <YOUR_PASSWORD>
Cacti Dashboard:
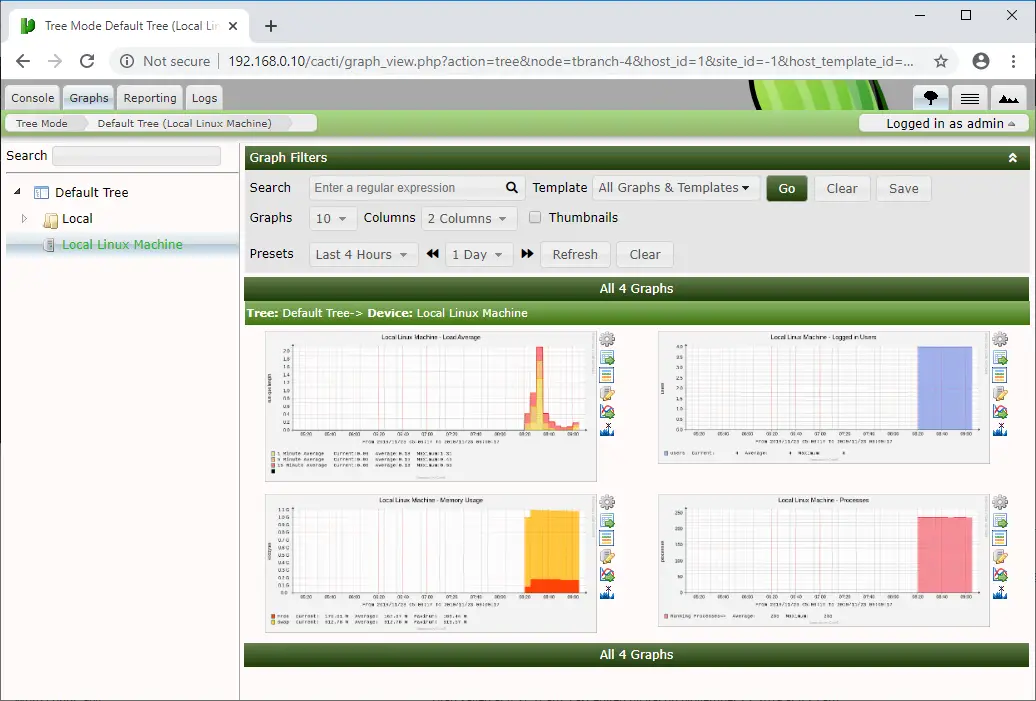
By default, the local machine (your Cacti server) will be added for monitoring in Cacti. You can Go to Graphs >> Default Tree >> Local Linux Machine to see the usage graph of the Cacti server.
Monitor Remote Linux Machines
READ: How to monitor remote Linux machines with Cacti monitoring tool
Conclusion
That’s All. I hope you have learned how to install Cacti on Ubuntu 18.04. Now, you can check out how to monitor remote Linux machines with Cacti monitoring tool. Please share your feedback in the comments section.